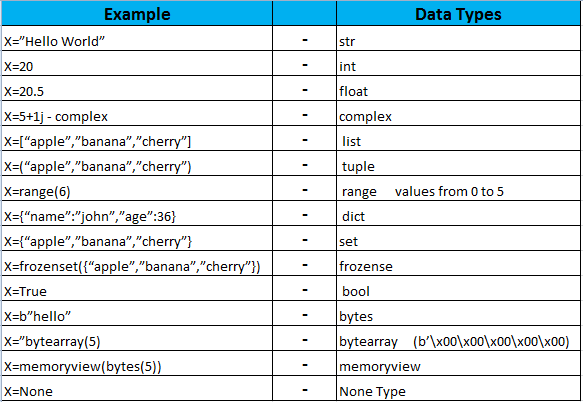
Chapter-2 Python Data types
Example 1: Arithmetic operators in python -Source Code
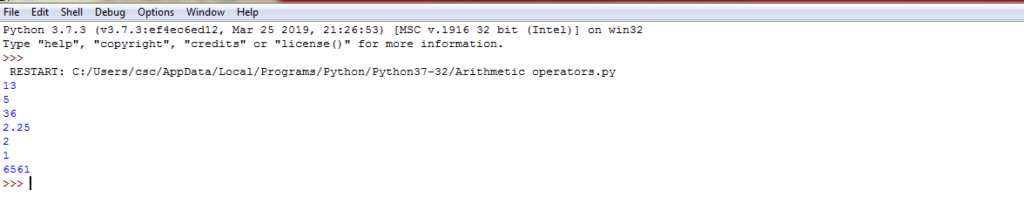
a=9 b=4 #Addition of numbers add=a+b #Subtraction of numbers sub=a-b #Multiplication of numbers mul=a*b #Division (float) of numbers div1=a/b #Division (floor) of numbers div2=a//b #Modulo of both numbers mod=a%b # Power p=a**b #print results print(add) print(sub) print(mul) print(div1) print(div2) print(mod) print(p)
Example 1: Arithmetic operators in python-Output
Example 2:Assignment operators in python -Source Code
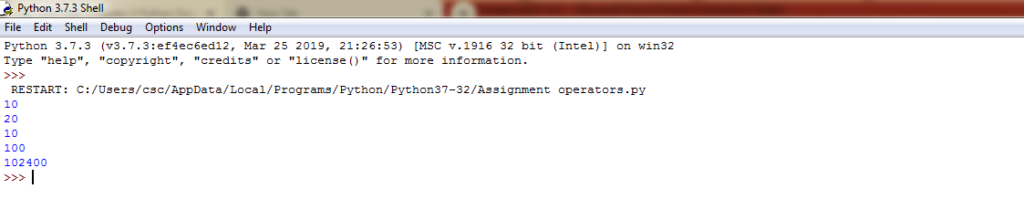
#Assign value a=10 #assign a variable b=a print(b) #Add and assign value b +=a print(b) #Substract and assign value b -=a print(b) #multiple and assign b *=a print(b) #bitwise left shift operator b <<=a print(b)
Example 2:Assignment operators in python -Output
Example 3:Logical operators in python -Source Code
a=True b=False #print a and b is false print(a and b) #print a or b is true print(a or b) #print not a is false print(not a)
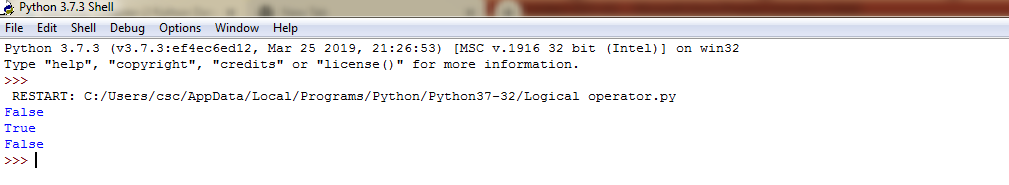
Example 3:Logical operators in python -Output
Example 4:Relational operators in python -Source Code
a=13 b=33 # a > b is false print(a > b) # a < b is true print(a < b) # a == b is false print(a == b) # a != b is true print(a != b) # a >=b is false print(a >=b) # a <= b is true print(a <= b)
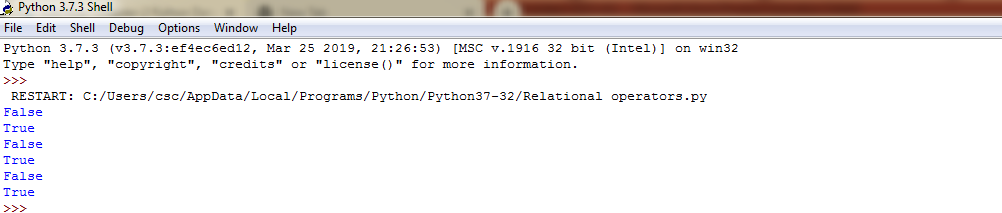
Example 4:Relational operators in python-Output
Example 5:Identity operator in python -Source Code
a=10 b=20 c=a print(a is not b) print(a is c)
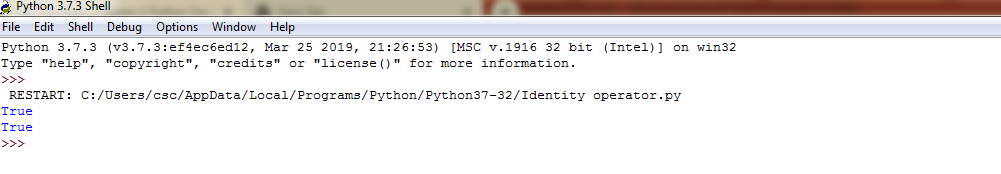
Example 5:Identity operator in python -Output
Example 6: Membership operator-Source Code
# python program to illustrate not ' in' operator
x=24
y=20
list=[ 10,20,30,40,50 ]
if (x not in list):
print("x is NOT present in given list")
else:
print("x is present in given list")
if(y in list):
print("y is present in given list")
else:
print("y is NOT present in given list")
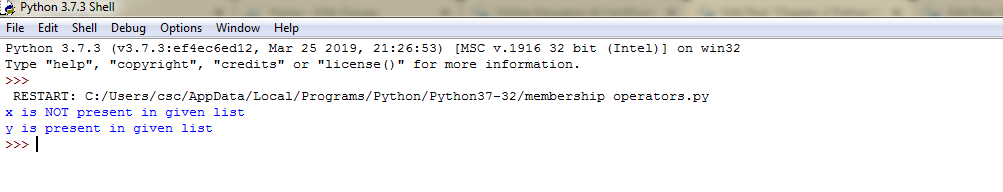
Example 6: Membership operator-Output
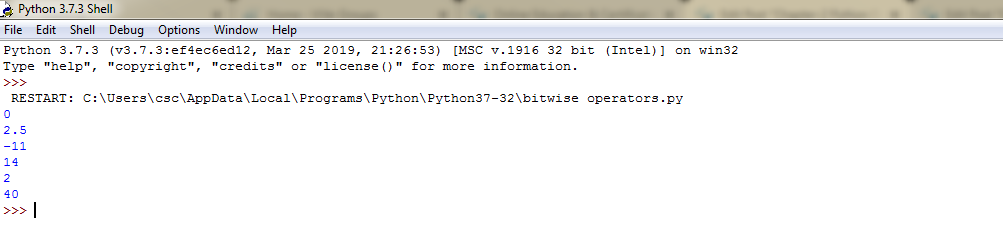
Example 7: Bitwise operator-Source Code
a=10 b=4 #print bitwise AND operation print(a&b) #print bitwise OR operation print(a/b) #print bitwise NOT operation print(~a) #print bitwise XOR operation print(a^b) #print bitwise right shift operation print(a>>2) #print bitwise left shift operation print(a<<2)
Example 7: Bitwise operator-Output
Example 8: operator precedence-Source Code
#Examples of operator precedence
#precedence of '+'&'*'* has higher precedence than +'
v=10+20*30
print(v)
#precedence of 'or'&'and' and has greater precedence than or so and is executed first
name = "kumar"
age= 0
if name == "kumar" or name == "ravi" and age >=2:
print("Hello! Welcome.")
else:
print("Good Bye!!")
Example 8: operator precedence-Output

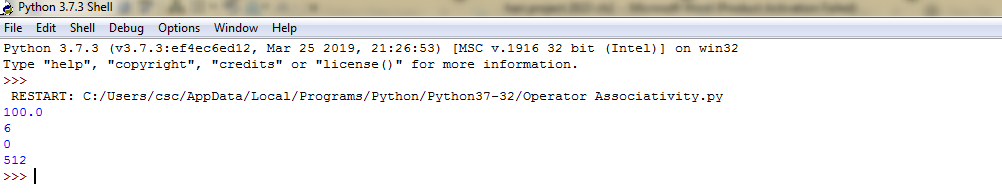
Example 9: Operator Associativity-Source Code
#left-right associativity #100/10*10 is calculated as #(100/10)*10 and not #as 100/(10*10) print(100/10*10) #left-right associativity #5-2+3 is calculated as #(5-2)+3 and not #as 5-(2+3) print(5-2+3) #left-right associativity print(5-(2+3)) #right-left associativity #2**3**2 is calculated as #2**(3**2) and not #as(2**3)**2 print(2**3**2)
Example 9: Operator Associativity-Output
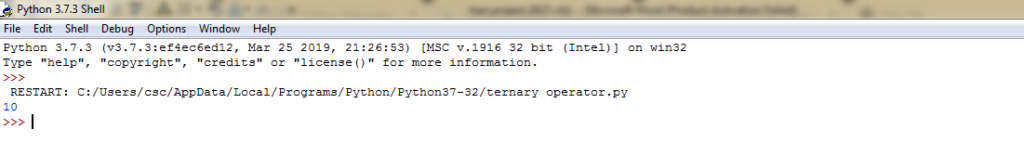
Example 10: Ternary operator-Source Code
#simple method to use ternary operator #program to demonstrate conditional operator a,b=10,20 #copy value of a in min if a<b else copy b min=a if a<b else b print(min)
Example 10: Ternary operator-Output
Direct method by using tuples,dictionary,and lambda
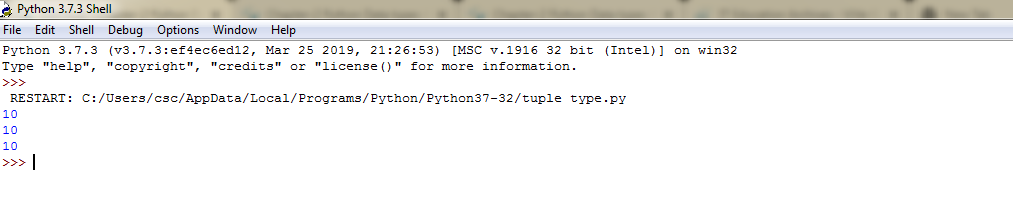
Example 11: Tuple Type-Source Code
#python program to demonstrate ternary operator
a,b=10,20
#use tuple for selecting an item
#if [a<b] is true it returns 1, so elements with 1 index will print
#else if [a<b] is false it returns 0, so elements with 0 index will print
print((b,a) [a<b])
#use dictionary for selecting an item
#if[a<b] is true then value of true key will print
#else if [a<b] is false then valse of false key will print
print({True:a,False:b} [a<b])
#lambda is more efficient than above two methods
#because in lambda we are assure that
#only one expression will be evaluated unlink in tuple or dictionary
print((lambda:b,lambda:a)[a<b]())
Example 11: Tuple Type-Source Code-Output
Ternary operator can be used as nested if-else also:-Source Code
#python program to demonstrate nested ternary operator
a,b=10,20
if a !=b:
if a>b:
print("a is grater than b")
else:
print("b is greater than a")
else:
print("both a and b are equal")
Ternary operator can be used as nested if-else also:-Output
To use print function in ternary operator-Source Code
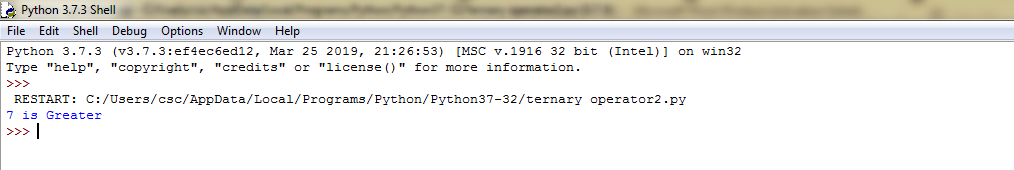
#Find the larger number among 2 using ternary operator in python3 a=5 b=7 #[statement_on_True] if [condition] else [statement _on_False] print(a, "is greater")if (a>b) else print(b,"is Greater")
To use print function in ternary operator-Output