Creating a Thread…
Example : ThreadDemo
import java.io.*;
class NewThread implements Runnable
{
Thread t;
NewThread()
{
t=new Thread(this,"Demo Thread");
System.out.println("Child thread:"+t);
t.start();
}
public void run()
{
try
{
for(int i=5;i>0;i--)
{
System.out.println("Child Thread:"+i);
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Child interrupted.");
}
System.out.println("Exiting child thread.");
}
}
class ThreadDemo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
new NewThread();
try
{
for(int i=5;i>0;i--)
{
System.out.println("Main Thread:"+i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Main thread interrupted.");
}
System.out.println("Main thread exiting.");
}
}
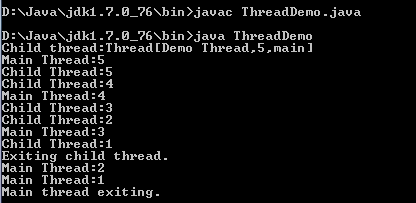 Output : ThreadDemo
Output : ThreadDemo
Extending Thread…
Example : ExtendThread
import java.io.*;
class NewThread extends Thread{
NewThread()
{
super("Demo Thread");
System.out.println("Child thread:"+this);
start();
}
public void run()
{
try
{
for(int i=5;i>0;i--)
{
System.out.println("Child Thread:"+i);
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Child interrupted.");
}
System.out.println("Exiting child thread.");
}
}
class ExtendThread
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
new NewThread();
try
{
for(int i=5;i>0;i--)
{
System.out.println("Main Thread:"+i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Main thread interrupted.");
}
System.out.println("Main thread exiting.");
}
}
 Output : ExtendThread
Output : ExtendThread
Using is Alive() and Join()…
Example : DemoJoin
import java.io.*;
class NewThread implements Runnable
{
String name;
Thread t;
NewThread(String threadname)
{
name=threadname;
t=new Thread(this,name);
System.out.println("New thread:"+t);
t.start();
}
public void run()
{
try
{
for(int i=5;i>0;i--)
{
System.out.println(name+":"+i);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println(name+"interrupted.");
}
System.out.println(name+"exiting.");
}
}
class DemoJoin
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
NewThread ob1=new NewThread("One");
NewThread ob2=new NewThread("Two");
NewThread ob3=new NewThread("Three");
System.out.println("Thread One is alive:"+ob1.t.isAlive());
System.out.println("Thread Two is alive:"+ob2.t.isAlive());
System.out.println("Thread Three is alive:"+ob3.t.isAlive());
try
{
System.out.println("Wainting for threads to finish.");
ob1.t.join();
ob2.t.join();
ob3.t.join();
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Main thread Interrupted");
}
System.out.println("Thread One is alive:"+ob1.t.isAlive());
System.out.println("Thread Two is alive:"+ob2.t.isAlive());
System.out.println("Thread Three is alive:"+ob3.t.isAlive());
System.out.println("Main thread exiting.");
}
}
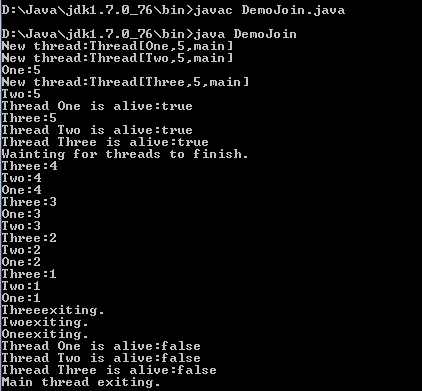 Output : DemoJoin
Output : DemoJoin
Synchronization…
Example : Synch
import java.io.*;
class Callme
{
void call(String msg)
{
System.out.println("["+msg);
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
class Caller implements Runnable
{
String msg;
Callme target;
Thread t;
public Caller(Callme targ,String s)
{
target=targ;
msg=s;
t=new Thread(this);
t.start();
}
public void run()
{
target.call(msg);
}
}
class Synch
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Callme target=new Callme();
Caller ob1=new Caller(target,"Hello");
Caller ob2=new Caller(target,"Synchrpnized");
Caller ob3=new Caller(target,"World");
try
{
ob1.t.join();
ob2.t.join();
ob3.t.join();
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
}
}
 Output : Synch
Output : Synch
The Synchronized Statement…
Example: Synch1
import java.io.*;
class Callme
{
void call(String msg)
{
System.out.println("["+msg);
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
}
class Caller implements Runnable
{
String msg;
Callme target;
Thread t;
public Caller(Callme targ,String s)
{
target=targ;
msg=s;
t=new Thread(this);
t.start();
}
public void run()
{
synchronized(target)
{
target.call(msg);
}
}
}
class Synch1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Callme target=new Callme();
Caller ob1=new Caller(target,"Bala");
Caller ob2=new Caller(target,"Tharun");
Caller ob3=new Caller(target,"Vital");
try
{
ob1.t.join();
ob2.t.join();
ob3.t.join();
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Interrupted");
}
}
}
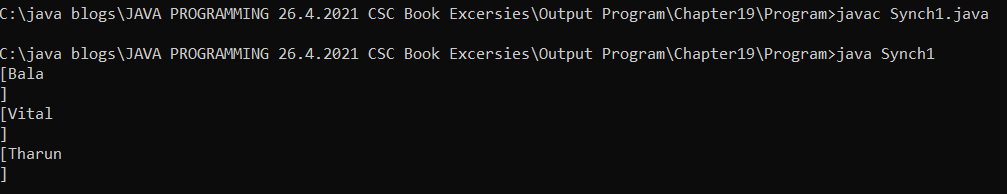 Output : Synch1
Output : Synch1
Thread Priorities…
Example 1 : HiLoPri
import java.io.*;
class clicker implements Runnable
{
int click=0;
Thread t;
private volatile boolean running=true;
public clicker(int P)
{
t=new Thread(this);
t.setPriority(P);
}
public void run()
{
while(running)
{
click++;
}
}
public void stop()
{
running=false;
}
public void start()
{
t.start();
}
}
class HiLoPri
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
clicker hi=new clicker(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY+2);
clicker lo=new clicker(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY-2);
lo.start();
hi.start();
try
{
Thread.sleep(10000);
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("Main thread interrupted.");
}
lo.stop();
hi.stop();
try
{
hi.t.join();
lo.t.join();
}catch(InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("InterruptedException caught");
}
System.out.println("Low-priority thread:"+lo.click);
System.out.println("High-priority thread:"+hi.click);
}
}
Example 2 : PC
import java.io.*;
class Q
{
int n;
synchronized int get()
{
System.out.println("Got:"+n);
return n;
}
synchronized void put(int n)
{
this.n=n;
System.out.println("Put:"+n);
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable
{
/*Thread t;
t=new Thread(this,"Producer");
t.set Priority(9);
t.start();*/
Q q;
Producer(Q q)
{
this.q=q;
new Thread(this,"Producer").start();
}
public void run()
{
int i=0;
while(true)
{
q.put(i++);
}
}
}
class Consumer implements Runnable
{
Q q;
Consumer(Q q)
{
this.q=q;
new Thread(this,"Consumer").start();
}
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
q.get();
}
}
}
class PC
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Q q=new Q();
new Producer(q);
new Consumer(q);
System.out.println("Press Control-C to stop.");
}
}
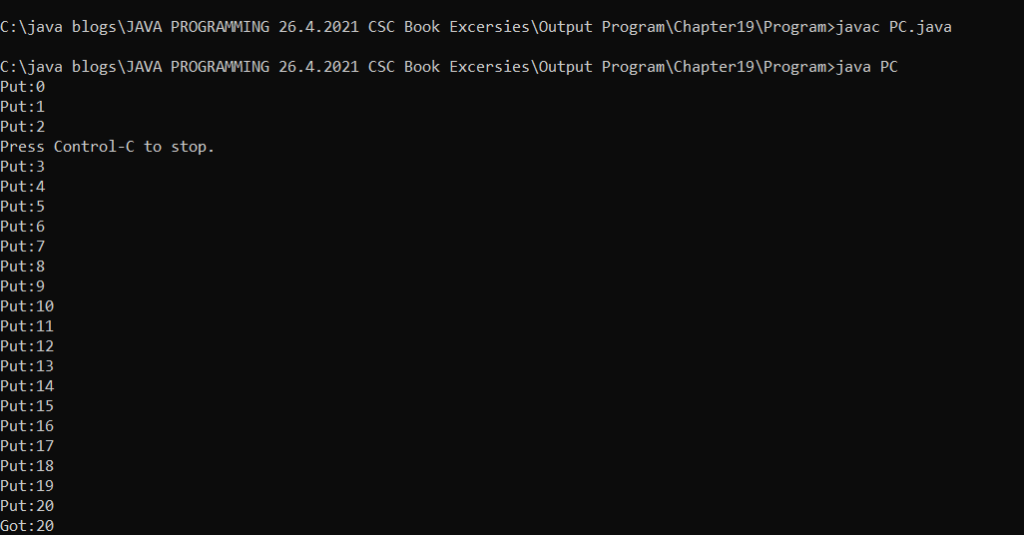 Output : PC
Output : PC







